According to well-known Cyber security companies and analytics, I have tried to encapsulate the trends that shape the cybersecurity landscape in 2021 and forecast toured 2022.

This breakdown into five significant trends covers most threats & attacks of cybersecurity 2021
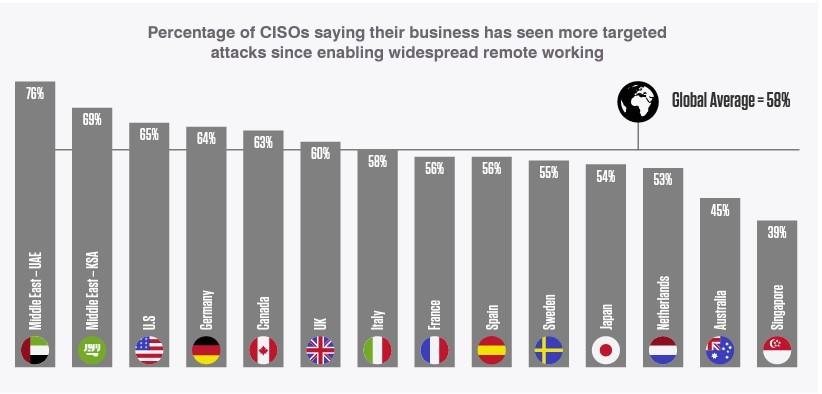
1. Working from home has become the new “normal” due to the COVID-19 pandemic
More and more businesses understand that while worrying about the Covid-19 pandemic, they still need to keep their business working and productive. Hackers understand the potential of this new “normal” and creatively start building attacks as a framework mimicking Covid-19 pandemic alerts, defense, and strategy. This connects us to the second trend.
2. Hackers keep on exploiting the Covid-19 crisis

Businesses allow employees to work from home or any other remote location (to keep the business functional), which creates a new threat as employees no longer operate under the same roof and network. Remote work spread so fast in the world that there was no time to investigate new threats and prepare a mature security structure in place.
3. Ransomware on COVID-19 Pandemic age.

Ransomware is one of the fastest-growing cyber security threats. When it comes to cybersecurity, ransomware has been one of the fastest-growing threats. Experts from Cybersecurity Ventures estimate that one attack will occur every 11 seconds in 2021
The impacts of a ransomware attack on businesses could include temporary and possibly permanent loss of your company’s data. Perhaps even a complete shutdown of business operations and financial loss due to the shutdown of revenue-generating operations.
4. Phishing COVID-19 Pandemic age

Now it is a fact! Covid-19 chaos-driven phishing/malicious URL attacks using fuzzy logic and data mining-based technologies. Anyone who uses email can be a target for phishing scammers. These days, if a user clicks on a phishing mail, it can go south with devastating results. Though good architectural security deployment might minimize the impact and/or block the phishing execution chain, it will be better to do proactive actions instead of Incident Management and Impact calculations (and more)
5. Malware COVID-19 Pandemic age

Understanding the definition of Malware: file or code, typically delivered over a network, infects, explores, steals, or conducts virtually any behavior an attacker wants. And because Malware comes in so many variants, there are numerous methods to infect computer systems.
The list of risks and threats above does not diminish the assertion of all of us that there are many threats and risks not mentioned here. Risks and threats such as Data Breaches, Compromised Passwords, Privilege Escalation, Botnet, Cobalt Strike, Supply Chain attacks, Exploit Vulnerability, Bypassing multi-factor authentication, Insider threats, SMS Attack, Browser-based attacks, Fake websites, and many, many, many more.

Cybersecurity risks and threats forecast toured 2022 during the COVID-19 age
I think you already understand that the COVID-19 will stay with us with no known expiration date. Hackers have not yet exhausted their abilities to find new features and a creative way that will look genuine and keep on challenging security, technology, and human resources.
1. Remote Work
As businesses realized that working from out of the office (Home, coffee shops, train stations, and more) on most business, effectiveness did not decrease, and in some, the effectiveness r. Even when forced to lay off employees, businesses adapt, and productivity was maintained by efficient, re-organized understanding. (This is one way to look at this). Remote work is here to stay and might get broader across countries and continents.
Therefore, some proactive and ongoing actions are suggested:
Block all poorly protected endpoints, lift the awareness of eHealth between employees, and add new restrictive policies to help reduce threat views using remote operational environments.
2. The exploitation of the COVID-19 crisis
Indeed, it was a state of affairs that organizations did not have time to organize. Between days, several employees across the world suddenly started working from home. And it was an opportunity that cybercriminals would never seize.
Therefore, some proactive and ongoing actions are suggested:
SOCs cannot cope due to a lack of unity among employees. Personal networks cannot be compared to centralized work environments from a security perspective, and so the growing integration of IoT devices suggests that businesses are in dire straits. ” Develop your visibility. In this regard, the need to implement SOAR-reminiscent IT visibility enhancement technologies is expected to become a serious trend in 2021 and in the years to come.
(SOAR stands for “Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response.” – Refers to technologies that enable organizations to collect inputs monitored by the security operations team. SOAR tools allow an organization to define incident analysis and response procedures in a digital workflow format.)
3. Ransomware ramp up – Wakeup Call
Cybersecurity experts believe that, in 2022, ransomware attacks will threaten business networks around the world. Following their 2021 success, the hacker will creatively find other technological ways to keep on the extortions.
The ongoing development with the improvement of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) will decrease the barrier to access for cybercriminals and make it less complicated to release ransomware assaults in opposition to predominant companies.
Familiarity with ransomware will be essential for most businesses in 2022.
Therefore, some proactive and ongoing actions are suggested:
Continuous improvement of Security Posture. Users’ education, rethink authentication, monitoring, alerting, backups, pinpoint solutions, and more
4. Phishing
Phishing is here to stay, and hackers are becoming more innovative and sophisticated. Phishing attacks more than doubled last year in 2022; it will continue to be a preferred method of attack for hackers.
Therefore, some proactive and ongoing actions are suggested:
Businesses need to be more proactive with their defense plans and budget accordingly to make sure anti-phishing solutions are in place. Additionally, cybersecurity training will need to evolve as the threats do. More innovative phishing campaigns, implement anti-phishing solutions and Enforce cybersecurity training and awareness. As businesses address security efforts and budget for employees’ ongoing security awareness and monitor this process, the Phishing attacks will decrease dramatically. This should be a business target achievement need to measure up to success.
5. Malware
With more attackers entering the market with malware-as-a-service campaigns, bad actors will continue to target every distributed workforce’s essential tools.
Therefore, some proactive and ongoing actions are suggested:
Evaluating newer anti-malware solutions and migrating to Endpoint Detect and Respond (EDR) solutions, which we’ve been advocating for years. However, even with these newer solutions, gaps still exist in many enterprises that allow ransomware attacks to occur, so improving security posture is essential. Keep researching for Malware defense solutions.

