Becoming a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023 will vary depending on the
organization’s specific requirements. However, certain skills and qualifications are commonly
expected for this role.

- Education: A bachelor’s degree in a related field, such as computer science, information technology, or information security, is typically required for a CISO position. Some organizations may prefer candidates with a master’s degree in a related field or a specific certification, such as a Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
- Technical expertise: A CISO should have a strong computer science and information technology foundation, with a thorough understanding of a wide range of technical topics related to information security. This may include knowledge of network security, application security, endpoint security, and cloud security.
- Leadership and management skills: A CISO will lead and coordinate a team of security professionals, so strong leadership and management skills are essential. This includes setting clear goals and expectations, delegating tasks effectively, and providing guidance and mentorship to team members.
- Communication skills: A CISO should be able to communicate effectively with both technical and non-technical stakeholders, including executives, board members, employees, and customers. This includes clearly and concisely explaining complex technical concepts to non-technical audiences.
- Problem-solving skills: A CISO should be able to quickly identify and resolve security issues as they arise, using a combination of technical expertise and critical thinking skills.
- Adaptability: The field of information security is constantly evolving, with new threats and technologies always emerging. A CISO should be able to adapt to these changes and stay up to date on the latest developments in the field.
- Business acumen: A CISO should have a strong understanding of the business goals and objectives of the organization and be able to develop information security strategies that support those goals. This includes the ability to understand the financial implications of security decisions and justify security investments to executives and the board of directors.
- Relationship-building skills: A CISO will likely work with various stakeholders within and outside the organization, so strong relationshipbuilding skills are important. This includes building trust and credibility with colleagues, customers, and partners and working effectively as a cross-functional team member.
- Industry-specific knowledge: Depending on the specific industry in which the organization operates, a CISO may need to know industry-specific regulations and standards. For example, a CISO in the healthcare industry may need to be familiar with HIPAA regulations. In contrast, a CISO in the financial industry may need to be familiar with PCI DSS requirements.
- Language skills: In a globalized business environment, it may be beneficial for a CISO to have proficiency in multiple languages to communicate effectively with stakeholders in different countries and regions.
In addition to these skills and qualifications, a CISO should also have a strong ethical
foundation and a commitment to upholding the organization’s values and mission. This
includes a deep understanding of the importance of information security and a commitment
to protecting the organization’s information assets.

To be a successful Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, an individual should have a range of characteristics and personal attributes that will enable them to lead and manage the organization’s information security program effectively. Here are some key characteristics that a CISO should have:

- Strategic thinking: A CISO should be able to develop and implement long-term plans for the organization’s information security program, considering the organization’s business goals and the changing threat landscape. This includes the ability to anticipate and prepare for future security challenges and to identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
- Strong communication skills: A CISO should effectively communicate with various stakeholders, including technical and non-technical audiences. This includes the ability to explain complex technical concepts clearly and concisely and to present information in a way that is easily understandable to others.
- Good problem-solving skills: A CISO should be able to quickly identify and resolve security issues as they arise, using a combination of technical expertise and critical thinking skills. This includes analyzing problems, considering a range of potential solutions, and choosing the most appropriate course of action.
- Adaptability: The field of information security is constantly evolving, with new threats and technologies always emerging. A CISO should be able to adapt to these changes and stay up to date on the latest developments in the field. This includes being open to learning new technologies and approaches and being willing to change course when necessary.
- Strong leadership skills: A CISO will lead and coordinate a team of security professionals, so strong leadership skills are essential. This includes setting clear goals and expectations, delegating tasks effectively, and providing guidance and mentorship to team members.
- Interpersonal skills: A CISO will likely work with various stakeholders within and outside the organization, so strong interpersonal skills are important. This includes building trust and credibility with colleagues, customers, and partners and working effectively as a cross-functional team member.
- Sound judgment: A CISO should be able to make informed decisions based on a thorough analysis of the situation and the available information. This includes weighing the risks and benefits of different options and choosing the course of action that is most likely to achieve the desired outcome.
- Ethical behavior: A CISO should have a strong ethical foundation and a commitment to upholding the organization’s values and mission. This includes a deep understanding of the importance of information security and a commitment to protecting the organization’s information assets.
- Resilience: As a CISO, you will likely face various challenges and setbacks. It is important to stay calm and focused under pressure and persevere in facing challenges.
- Passion for information security: A successful CISO should have a genuine passion for information security and a desire to impact this field positively. This includes a willingness to learn and improve continuously and a dedication to staying at the forefront of the field.
In addition to their technical expertise, a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023
should also have a range of to be effective in their role. These skills are necessary to align the
organization’s information security program with the business goals and objectives and
effectively communicate information security’s value to non-technical stakeholders. Here are
some key business skills that a CISO should have:

- Business acumen: A CISO should have a strong understanding of the business goals and objectives of the organization and be able to develop information security strategies that support those goals. This includes understanding the financial implications of security decisions and being able to justify security investments to executives and the board of directors.
- Strategic thinking: A CISO should be able to develop and implement long-term plans for the organization’s information security program, considering the organization’s business goals and the changing threat landscape. This includes the ability to anticipate and prepare for future security challenges and to identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
- Communication skills: A CISO should effectively communicate with various stakeholders, including technical and non-technical audiences. This includes the ability to explain complex technical concepts clearly and concisely and to present information in a way that is easily understandable to others.
- Relationship-building skills: A CISO will likely work with various stakeholders within and outside the organization, so strong relationship-building skills are important. This includes building trust and credibility with colleagues, customers, and partners and working effectively as a cross-functional team member.
- Negotiation skills: A CISO may need to negotiate with vendors, partners, and other stakeholders to secure the resources and support needed to implement the organization’s information security program. This includes identifying the needs and interests of the other party and finding mutually beneficial solutions.
- Budget management skills: A CISO may be responsible for managing the budget for the organization’s information security program, so it is important to have strong financial management skills. This includes the ability to develop and stick to a budget, prioritize expenditures, and track and report on budget performance.
- Project management skills: A CISO may be responsible for leading and coordinating complex projects related to implementing the organization’s information security program. This includes defining project scope and objectives, developing and executing a project plan, and managing resources and stakeholders effectively.
- Risk management skills: A CISO should be able to identify and assess potential risks to the organization’s information assets and develop strategies to mitigate those risks. This includes knowledge of risk assessment methodologies and risk management frameworks such as ISO 27001 and NIST 800-53.
- Compliance skills: A CISO should know the various laws, regulations, and industry standards that apply to the organization and ensure that the organization’s information security program complies with these requirements. This may include knowledge of topics such as data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA), cybersecurity regulations (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS), and industry-specific standards (e.g., NIST Cybersecurity Framework for critical infrastructure).
- Leadership skills: A CISO will be responsible for leading and coordinating a team of security professionals, so strong leadership skills are essential. This includes setting clear goals and expectations, delegating tasks effectively, and providing guidance and mentorship to team members.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, it is important to have a wide range of
to develop and implement the organization’s information security program effectively. These
skills are necessary to identify and assess potential threats and vulnerabilities and to
implement the appropriate controls to protect the organization’s information assets. Here
are some key technical skills that a CISO should have:

- Cybersecurity expertise: A CISO should have a thorough understanding of the various types of cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities that organizations face and the technologies and best practices that can be used to protect against these threats. This includes knowledge of network security, application security, endpoint security, and cloud security.
- Security operations skills: A CISO should have a thorough understanding of the various processes and technologies involved in security operations, including incident response, vulnerability management, and security monitoring. This includes knowledge of tools and techniques for detecting and responding to security incidents and best practices for maintaining the security of an organization’s systems and data.
- ldentity and access management skills: A CISO should know the various technologies and processes involved in managing user identities and access to systems and data. This includes knowledge of authentication, authorization, single sign-on, and multi-factor authentication.
- Security architecture and design skills: A CISO should understand the principles of secure architecture and design and be able to apply these principles to the development of secure systems and networks. This includes knowledge of secure coding practices, communication protocols, and system architecture.
- Threat intelligence skills: A CISO should be able to gather, analyze, and act on intelligence about potential threats to the organization’s information assets. This includes knowledge of threat intelligence sources, such as open source, technical, and human intelligence, and tools and techniques for analyzing and disseminating this intelligence.
- Data privacy skills: A CISO should have a strong understanding of the various issues related to data privacy, including the proper handling and protection of personal data and the legal and regulatory requirements that apply. This may include knowledge of data classification, data governance, data retention, and data breach notification.
- Security analytics skills: A CISO should know the various tools and techniques used for security analytics, including log analysis, security data visualization, and machine learning. This includes the ability to use these tools to identify patterns and trends in security data and to use this information to improve the effectiveness of the organization’s security program.
- Cloud security skills: With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, a CISO must have a strong understanding of cloud security issues and best practices. This includes knowledge of cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud infrastructure security, and cloud data protection.
- DevSecOps skills: As organizations adopt more agile development methodologies, a CISO needs to understand DevSecOps principles and practices. This includes knowledge of continuous integration, continuous delivery, automated testing, and integrating security into the software development lifecycle.
- Programming skills: While it is not necessarily expected for a CISO to be a proficient programmer, it can be helpful to have a basic understanding of programming concepts and languages to communicate effectively with developers and understand the technical aspects of the organization’s security program.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, you will have a range of focused on
protecting the organization’s information assets and ensuring compliance with relevant laws,
regulations, and industry standards. Here are some key responsibilities that a CISO may have:
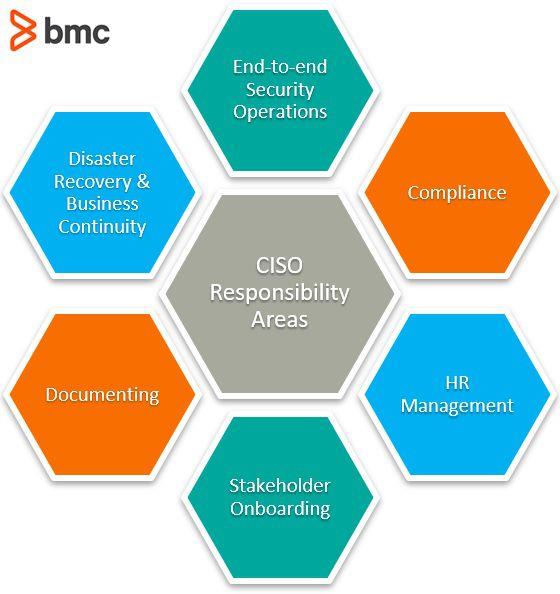
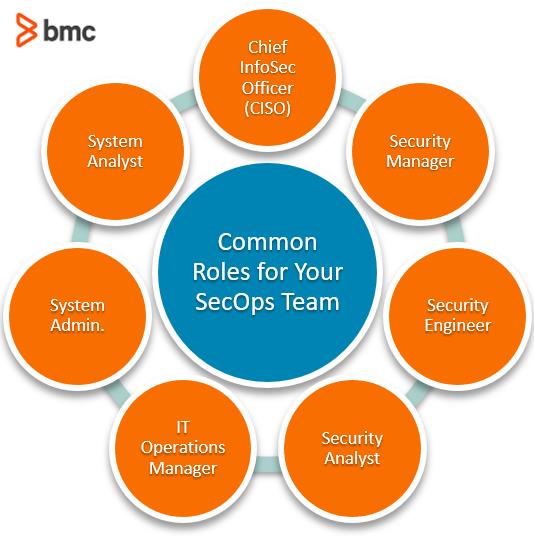
- Develop and implement the organization’s information security program: This includes creating policies, procedures, and standards related to information security, as well as identifying and implementing appropriate controls to protect the organization’s information assets.
- Lead and coordinate the organization’s security team: As the leader of the security team, you will be responsible for setting goals and expectations, assigning tasks, and providing guidance and mentorship to team members.
- Stay current on the latest security threats and technologies: It is important to continuously monitor the threat landscape and stay informed about new threats and technologies that may impact the organization. This may include subscribing to security alerts and bulletins, attending security conferences and seminars, and participating in industry groups and forums.
- Manage security risks: As a CISO, you will be responsible for identifying and assessing potential risks to the organization’s information assets and developing strategies to mitigate those risks. This may include conducting risk assessments, implementing security controls, and developing incident response plans.
- Oversee compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards: Depending on the specific industry in which the organization operates, there may be a range of laws, regulations, and standards that apply to the organization’s information security program. As the CISO, you will be responsible for ensuring that the organization is compliant with these requirements.
- Communicate with stakeholders: As the organization’s security leader, you must communicate effectively with a wide range of stakeholders, including executives, board members, employees, customers, and partners. This may include presenting security reports and updates to the board, providing guidance and support to employees, and working with customers and partners to ensure the security of shared systems and data.
- Manage security budgets and resources: Depending on the size and complexity of the organization’s security program, you may be responsible for managing budgets and resources for security initiatives. This includes developing and managing a security budget, identifying and allocating resources to support security projects, and tracking and reporting on budget and resource utilization.
- Conduct security audits and assessments: As part of the organization’s security program, you may be responsible for conducting regular security audits and assessments to ensure the effectiveness of the organization’s security controls. This may include performing vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and other types of testing to identify and address weaknesses in the organization’s security posture.
- Respond to security incidents: In a security incident, you will be responsible for leading the organization’s response efforts, which may include coordinating with the security team and other stakeholders, communicating with customers and partners, and implementing incident response plans.
- Promote security awareness and education: As a CISO, you will be responsible for promoting security awareness and education within the organization, including training employees on security best practices and providing guidance on identifying and reporting potential threats. This may include developing and delivering security awareness training programs and creating resources and materials to support ongoing security education efforts.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, it is important to have a wide range of
to develop and implement the organization’s information security program effectively. This
includes knowledge of technical topics related to cybersecurity and information technology,
as well as business skills and industry-specific regulations and standards. Here are some key
areas of knowledge that a CISO should have:

- Cybersecurity: A CISO should thoroughly understand the various types of cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities that organizations face and the technologies and best practices that can be used to protect against these threats. This may include knowledge of network security, application security, endpoint security, and cloud security.
- Security operations: A CISO should have a thorough understanding of the various processes and technologies involved in security operations, including incident response, vulnerability management, and security monitoring. This includes knowledge of tools and techniques for detecting and responding to security incidents and best practices for maintaining the security of an organization’s systems and data.
- Identity and access management: A CISO should know the various technologies and processes involved in managing user identities and access to systems and data. This includes knowledge of authentication, authorization, single sign-on, and multi-factor authentication.
- Security architecture and design: A CISO should understand the principles of secure architecture.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, you will lead and coordinate the
organization’s information security program and manage and develop a team of security
professionals. To be an effective leader, it is essential to have various leadership skills and
qualities. Here are some key areas of leadership that a CISO should focus on:

- Strategic thinking: As a CISO, developing and implementing long-term plans for the organization’s information security program is essential, considering its business goals and the changing threat landscape. This includes the ability to anticipate and prepare for future security challenges and to identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
- Communication skills: A CISO should be able to communicate effectively with a wide range of stakeholders, including technical and non-technical audiences. This includes the ability to explain complex technical concepts clearly and concisely and to present information in a way that is easily understandable to others.
- Relationship-building skills: A CISO will likely work with various stakeholders within and outside the organization, so strong relationship-building skills are important. This includes building trust and credibility with colleagues, customers, and partners and working effectively as a cross-functional team member.
- Change management skills: As a CISO, you may be responsible for leading organizational change, particularly in information security. This includes the ability to identify the need for change, develop and communicate a vision for change, and lead others through the process of implementing and adapting to change.
- Team management skills: As the leader of the security team, you will be responsible for setting goals and expectations, assigning tasks, and providing guidance and mentorship to team members. This includes delegating effectively, providing constructive feedback, and creating an environment that fosters teamwork and collaboration.
- Conflict resolution skills: As a CISO, you may be called upon to mediate conflicts that arise within the security team or between the security team and other stakeholders. This includes identifying the root causes of conflicts, facilitating dialogue and negotiation, and helping parties reach mutually satisfactory resolutions.
- Coaching and mentorship skills: As a CISO, you will have the opportunity to help develop the skills and careers of your team members. This includes providing guidance and support, identifying improvement areas, and creating development plans that help team members achieve their career goals.
- Decision-making skills: A CISO will be called upon to make a wide range of decisions, often under time pressure and with incomplete information. It is important to be able to analyze the situation and make informed decisions based on the available information. This includes weighing the risks and benefits of different options and choosing the course of action most likely to achieve the desired outcome.
- Adaptability: The field of information security is constantly evolving, with new threats and technologies always emerging. A CISO should be able.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, it is important to have a clear for the
organization’s information security program aligned with its overall business goals and
objectives. This vision should be forward-looking, anticipate the organization’s future needs
and challenges, and be responsive to the changing threat landscape. Here are some key
elements of a vision for a 2023 CISO:

- Risk management: A CISO’s vision should prioritize risk management, recognizing that information security is ultimately about protecting the organization’s assets and minimizing the impact of potential threats. This includes developing a robust risk management program that identifies and assesses potential risks to the organization’s information assets and implements controls to mitigate those risks.
- Compliance: Depending on the specific industry in which the organization operates, there may be a range of laws, regulations, and standards that apply to the organization’s information security program. A CISO’s vision should include ensuring compliance with these requirements while recognizing that compliance is only one aspect of a comprehensive security program.
- Continuous improvement: A CISO’s vision should focus on continuous improvement, recognizing that the threat landscape is constantly evolving and that the organization’s security program must evolve. This includes regularly reviewing and updating policies, procedures, and controls, as well as investing in the development and training of the security team.
- Collaboration: A CISO’s vision should recognize the importance of collaboration, both within the security team and with other stakeholders within and outside the organization. This includes building strong relationships with colleagues, customers, and partners and working effectively as a cross-functional team member.
- Innovation: A CISO’s vision should focus on innovation, recognizing that information security is a rapidly evolving field and that the organization needs to be open to new ideas and approaches. This includes exploring new technologies and best practices and fostering a culture of innovation within the security team.
- Communication: A CISO’s vision should focus on effective communication, recognizing that security is everyone’s responsibility and that all stakeholders should understand their role in protecting the organization’s assets. This includes developing and implementing strategies for communicating with different audiences, such as employees, customers, and partners and creating resources and materials to support ongoing security education efforts.
- Culture: A CISO’s vision should focus on building a strong security culture within the organization, recognizing that employees’ attitudes and behaviors can significantly impact the organization’s security. This includes promoting a security awareness and responsibility culture and providing training and resources to help employees understand and meet their security responsibilities.
- Business alignment: A CISO’s vision should be aligned with the organization’s overall business goals and objectives, recognizing that information security is not an end. Still, a means to support the success of the business. This includes developing a security program that is responsive to the needs of the business and that effectively communicates
As a new Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, it is important to take a structure
to your first 90 days to quickly get up to speed and positively impact the organization’s
information security program. Here are some key steps that a new CISO should take during
this initial period:

- Assess the current state of the organization’s security program: The first step in your new role should be to thoroughly understand its current security posture, including its strengths and weaknesses. This may include reviewing existing policies, procedures, and controls and conducting a risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Meet with key stakeholders: During your first 90 days, it is important to establish relationships with key stakeholders within and outside of the organization. This may include meeting with executives, board members, employees, customers, and partners to introduce yourself and understand their perspectives on information security.
- Understand the organization’s business goals and objectives: To align its security program with its business goals effectively, it is important to understand its overall business strategy and objectives. This may include meeting with business leaders and reviewing business plans and documents.
- Identify areas for improvement: Based on your assessment of the current state of the organization’s security program and your understanding of the organization’s business goals and objectives, you should be able to identify areas where the security program can be improved. This may include updating policies and procedures, implementing new controls, or investing in new technologies or training.
- Communicate your vision and plan: Once you have identified areas for improvement, it is important to develop a plan to address these issues and communicate this plan to key stakeholders. This may include presenting your vision and plan to the board of directors or senior leadership and communicating with employees and other stakeholders about the changes.
- Build and develop the security team: As the security team leader, it is important to establish your leadership style and set clear goals and expectations for team members. This may include recruiting and hiring new team members and providing guidance and support to existing team members to help them develop their skills and careers.
- Foster a culture of security awareness: One of the key responsibilities of a CISO is to promote security awareness and responsibility within the organization. During your first 90 days, you should develop and implement strategies for building a strong security culture, including creating resources and materials to support ongoing security education efforts and training employees on security best practices.
- Review and update incident response plans: It is important to have robust incident response plans in place in the event of a security incident. Reviewing and updating these plans during your first 90 days in the role is a good idea. This may include identifying and testing the roles and responsibilities of different team members and testing and practicing incident response scenarios.
- Stay current on the latest security threats and technologies: As a CISO, it is important to continuously monitor the threat landscape and stay informed about new threats and technologies that may impact the organization. This may include subscribing to security alerts and bulletins, attending security conferences and seminars, and participating in industry groups and forums.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, you must understand to whom you will
report and how your role fits into the overall organizational structure. Here are some
common options for to whom a CISO may report:

- The CEO or President: In some organizations, the CISO may report directly to the CEO or President, particularly in smaller organizations or those where information security is a top priority. Reporting to the CEO or President allows the CISO to have a direct line of communication with the organization’s top leadership and to be involved in strategic decision-making.
- The Chief Information Officer (CIO): In many organizations, the CISO may report to the CIO, who manages the organization’s information technology. Reporting to the CIO allows the CISO to work closely with other IT leaders and be involved in developing and implementing the organization’s overall IT strategy.
- A separate division or unit: The CISO may report to a separate division or unit responsible for information security in some organizations. This could be a stand-alone information security division or part of a larger division such as risk management or compliance.
- The board of directors: In some cases, the CISO may report directly to the board of directors, particularly in organizations where the board has a particular interest in or oversight of the organization’s information security program. Reporting to the board allows the CISO to provide regular updates and to have a direct line of communication with the organization’s top leadership.
No matter to whom the CISO reports, it is vital to establish a strong working relationship with this individual or group and to be able to effectively communicate the value and importance of the organization’s security program. It is also essential to understand the expectations and priorities of the person or group to whom you are reporting and to align your activities and priorities with the overall goals and objectives of the organization.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, you will be responsible for leading and
coordinating the organization’s information security program, which may involve interacting
with C-level management and technical IT staff. Here are some key considerations for how a
CISO should approach these interactions:

- Interacting with C-level management: As a CISO, you may be called upon to interact with Clevel executives such as the CEO, CFO, and COO, as well as with the board of directors. It is important to effectively communicate the value and importance of the organization’s security program to these stakeholders and to present technical concepts in a way that is easily understandable to non-technical audiences. You should also be prepared to answer questions and address these stakeholders’ concerns about the security program.
- Interacting with technical IT staff: As a CISO, you must also interact with technical IT staff, such as network administrators, system administrators, and security analysts. It is important to establish strong working relationships with these individuals and to be able to communicate effectively about technical security issues. This may include providing guidance and support to technical staff and coordinating with them on implementing and maintaining security controls.
- Providing guidance and direction: As the security team leader, you will provide guidance and direction to C-level management and technical IT staff. This includes setting goals and expectations for team members, providing regular updates on the status of the security program, and communicating any changes or updates to policies or procedures.
- Facilitating communication and collaboration: As a CISO, you may be called upon to facilitate communication and collaboration between C-level management and technical IT staff. This may include serving as a bridge between these two groups and helping to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the goals and objectives of the security program and are working towards the same objectives.
- Balancing the needs of the business with the needs of security: As a CISO, you will need to balance the needs of the business with the needs of security, recognizing that the organization’s security program is ultimately a means to support the success of the business. This may involve working with business leaders to understand their goals and priorities and finding ways to align the security program with these objectives while ensuring that the organization’s assets are adequately protected.
- Building trust and credibility: To be effective in your role, it is important to build trust and credibility with C-level management and technical IT staff. This may include demonstrating your technical expertise, being responsive to the organization’s needs, and being transparent about the security program and any potential risks or vulnerabilities.
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, you will be responsible for developing
and implementing the organization’s information security program and providing regular
updates and reports on the program’s status to key stakeholders. Here are some common
annual deliverables that a CISO may be expected to provide to the organization:

- A security roadmap: A security roadmap is a long-term plan for the organization’s information security program, outlining the key goals and objectives for the program and the steps that will be taken to achieve those objectives. A security roadmap may include a timeline for implementing new controls or technologies, as well as plans for ongoing maintenance and improvement of the security program.
- A security budget: A security budget is a detailed plan for how the organization’s security resources will be allocated over the year. This may include funding for new technologies, training, or staff and ongoing expenses such as maintenance and support.
- A risk assessment: A risk assessment is an evaluation of the potential risks that the organization faces concerning its information assets and the likelihood and impact of those risks. A risk assessment may include an analysis of the organization’s current security controls and a recommendation additional controls or measures to mitigate identified risks.
- A security incident report: A security incident report is a detailed account of any security incidents that occurred over the course of the year, including the nature of the incident, the impact on the organization, and the steps taken to mitigate the incident. This report may also include recommendations for improving the organization’s incident response capabilities.
- A security awareness report: A security awareness report is a summary of the security awareness efforts that were undertaken over the course of the year, including
As a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) in 2023, you will lead and coordinate the
organization’s information security program, which may involve various activities and
responsibilities. Here is a summary of some of the key operations and critical issues that a
CISO may be expected to manage:
- Developing and implementing the security program: This may include creating and updating policies and procedures, implementing controls to protect the organization’s assets, and managing the budget and resources for the security program.
- Conducting risk assessments: This may include identifying and assessing potential risks to the organization’s information assets and implementing controls to mitigate those risks.
- Responding to security incidents: This may include developing and implementing incident response plans, coordinating with technical staff and other stakeholders in the event of an incident, and reporting on the nature and impact of the incident.
- Promoting security awareness: This may include creating and distributing materials to educate employees and other stakeholders about security best practices and providing training and resources to help employees understand their role in protecting the organization’s assets.
- Building and developing the security team: This may include recruiting and hiring new team members, providing guidance and support to existing team members, and setting goals and expectations for the team.
- Managing vendor relationships: This may include working with external vendors and partners to ensure that the organization’s security needs are met and negotiating contracts and agreements that align with the organization’s security objectives.
- Staying current on the latest security threats and technologies: This may include subscribing to security alerts and bulletins, attending security conferences and seminars, and participating in industry groups and forums to stay informed about new threats and technologies.
Some critical issues that a CISO may need to address include:
- Cybersecurity threats: A CISO may need to constantly monitor the threat landscape and identify and respond to potential threats to the organization’s assets.
- Compliance: Depending on the specific industry in which the organization operates, there may be a range of laws, regulations, and standards that apply to the organization’s security program. A CISO may need to ensure compliance with these requirements while also balancing the needs of the business.
- Data privacy: A CISO may need to be involved in managing and protecting sensitive data, including ensuring that the organization complies with data privacy regulations and that appropriate controls are in place to protect personal data.
- Business continuity: A CISO may need to develop and implement plans to ensure that the organization can continue operating in the event of a security incident or other disruption.
- Budget constraints: A CISO may need to manage the security budget and decide how to allocate resources to maximize the security program’s effectiveness.
- Talent retention: A CISO may need to work to retain and develop the skills of the security team, recognizing that the information security field is constantly evolving and that team members may need ongoing training and development to stay current.